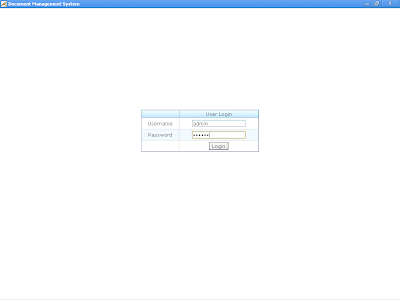
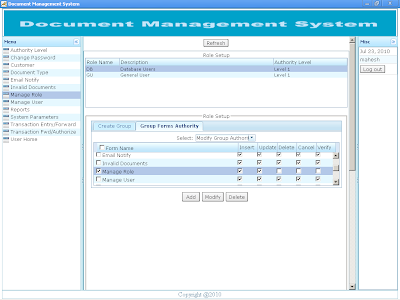
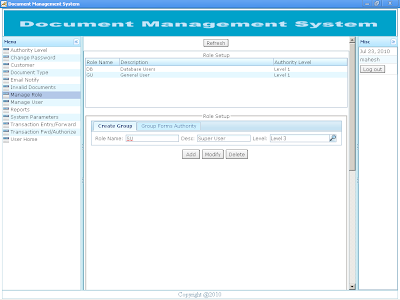
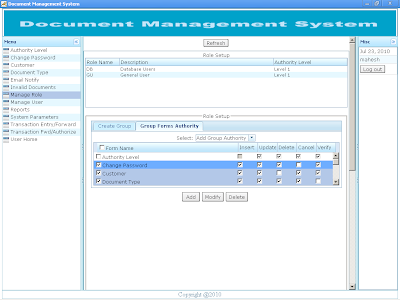
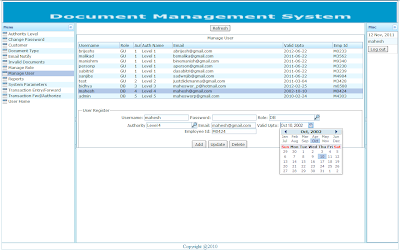
Registered user can login to the application through their user name and password. The URL can be obtained from the system administrator of Document Management System. |
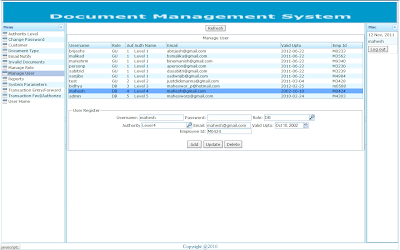
Customer Registration Customers involved in the business process can be registered. This helps in generating report based on the customer identity. |
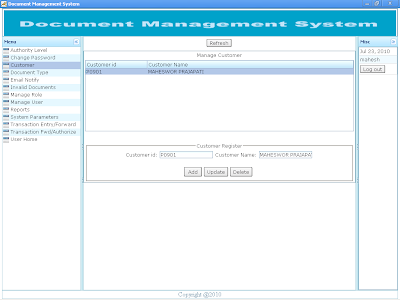
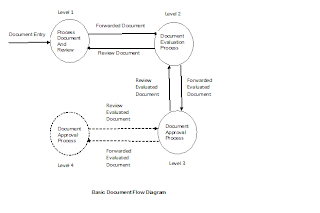
Document Transaction Steps and flow diagram 1. Document Entry. 2. Document Forward. 3. Document Review. 4. Document Authorize. 5. Document Reject |
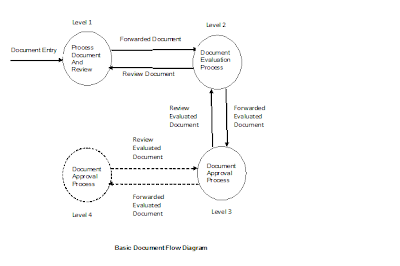
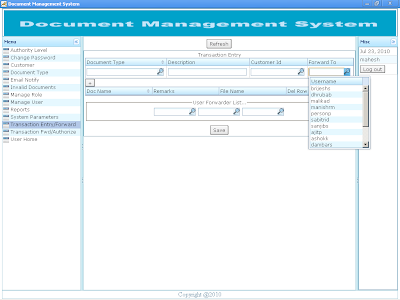
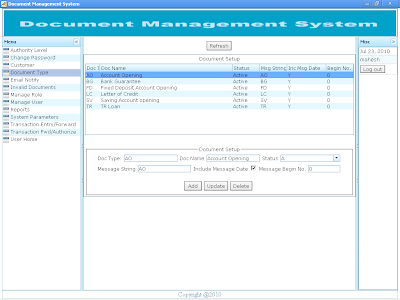
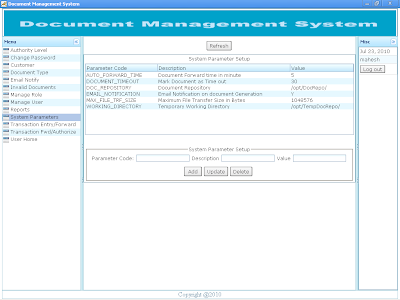
Document Transaction Generation This is the document transaction generation module. In the screen shot Document Type, Customer list and forwarder lists is auto populated from the initial setups. User can select appropriate values from the list to generate document transaction. A document may contain multiple files as shown below in the screen shot. Some Useful Notes: 1. Document Type is user defined and parameterized document. It helps to differentiate the type of document generated. As per the configuration, a document number may contain document short string, document date and document serial number.eg AO060720100000000019. 2. “Forward To” user field is the default user the document to be forwarded to. It must not be empty. The block “User Forwarder List” contain list of users in the priority list to be forwarded one by one from left side simultaneously. If a default user, that is user in “Forward To” field do not respond within DOCUMENT TIME OUT (DOCUMENT_TIMEOUT) parameter default set to 30 minutes, then the document is revoked from “Forward To” user (admin) and auto forwarded to first user in User “Forwarded List” (surendras). If “surendars” do not respond within DOCUMENT TIME OUT, then the document is revoked from the user and auto forwarded to user “dhrubab”. During the document auto forward process, whenever any one of the user (admin, surendras, dhrubab or malikad) respond, the users in the forwarder chain are cancelled from the priority list. Then the document is processed as per the action (FORWARD, REVOKE, AUTHORIZE, REJECT) taken by the forwarder user. 3. Document No: It is system generated number to uniquely identify the document being generated. Document number generated depends upon the configuration of document type definition. A Document Number can contain multiples related files with the document. Screen shot show a Bank Guarantee document that contain citizen ship certificate and guarantee fill up form in portable document format. 4. + sign button indicates the addition of the file in the document to be generated. Clik on the + sign button to add new row to the document. 5. – sign button on each row indicates the deletion of the file from the document. Click on the –sign button to delete the current row from the document. 6. Remarks on the each document can be included in the remarks field that should be informative to the user receiving the document. Remarks are also show on document flow report. 7. The application supports files names in portable document format (PDF) for preview during document processing. Files in other formats are not available for preview but they can be downloaded to the local computer and opened as per user demand. It is suggested to process files in portable document format as the time to generate preview for portable document format is much lesser than file downloads. Avoid processing document files other than portable document format (PDF) to minimize bandwidth usage. 8. Extensions of filenames are mandatory in “File Name” field. The system returns error and file could not be transmitted if extension are avoided. For instance, if only name of file “citizen” is placed in “File Name” field, application would return error during file upload process. So, it is required to enter extension of the file with their file name that is “citizen.pdf” in “File Name” field. 9. Files must be stored in Application Home Directory default to “C:\docman”. The default Application Home Directory can be changed upon request to the administrator. 10. “Save” Button saves the files and generates a unique Document Number for transaction. 11. Email alert is sent to the default user (admin) upon Document Transaction Generation. 12. Refer to the screen shot shown below. Screen shot of Document Transaction Entry: |
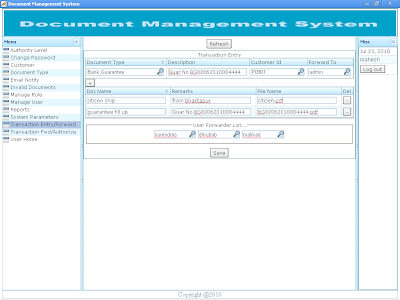
Document Forward/Revoke/Authorize/Reject The Document Authorize/Forward/Reject/Review grid shows the list of document forwarded to login user for approval. Click on the record to display the details of the document. Document file in portable document format (PDF) can be previewed while other file formats need to be downloaded to the local computer. As per the requirement, a document can be processed for: 1. REVIEW document. 2. FORWARD for next level approval. 3. AUTHORIZE document. 4. REJECT document. |
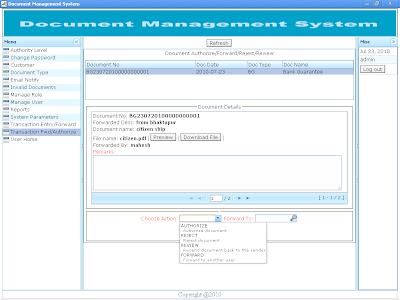
User Actions: 1. REVIEW Document Whenever modification is required in the document, it is sent for review. User performing review can be same user that forward the document or any other user in the user list. 2. FORWARD Document Whenever approval is sought from next authority level, then the document is forwarded to the respective user. 3. AUTHORIZE Document Permit the document to carry on the business process. 4. REJECT Documents Disallow to process the business activity. A remark is mandatory while processing the document. The document recipient can track the state of the document and business process from the remarks as well. So, remarks must be precise and clear that can be taken as reference to authenticate the document. Remarks are also shown on document flow report. Screen shot of File preview |
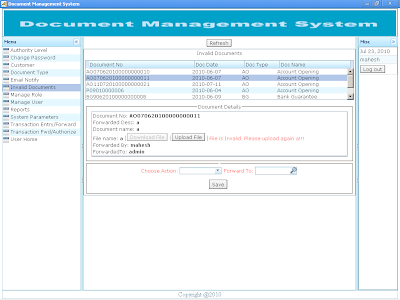
Invalid Documents: During document transaction processing, if file name specified in file name field does not exist in Application Home Directory, the resulting document number is marked as Invalid Document. Invalid Documents can be processed from Invalid Document menu from “Invalid Document” Grid as show in the screen shot below. Respective files can be placed in Application Home Directory and process “Upload File” button to validate the resulting document. |
Email Notification and Alerts Email Notification in the form of alerts is sent to the user that have been forwarded a document or sent for review. During AUTHORIZE and REJECT of document, email is sent to all the users involved for the document processing. This will help user to know the state of the document as well. Background process for Auto Email Notification can be started and stopped from Email Notify menu. |
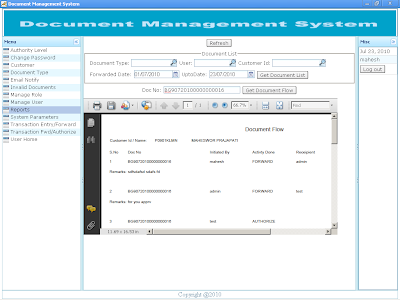
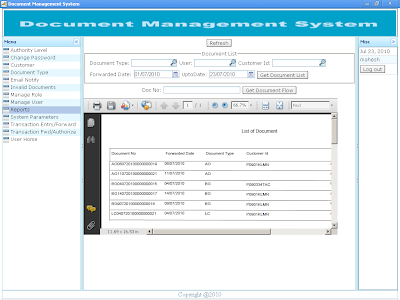
User Reports Reports are embedded in the application and rendered in Portable Document Format (pdf). Screen shot of List of Documents |
Screen shot of Document Flow Report |